The world has changed. We cannot go back to where we were, nor continue to head in the same direction we were set upon before this crisis. But that is easier said than done and will be impossible if we do not embrace the grief of what we are journeying through together. There has been and continues to be painful loss. We have lost dear friends, family members, neighbours and colleagues. We have lost jobs, income, holidays and social gatherings. We have missed births and birthdays, key social events, final goodbyes and funerals. We are bereaved of whole ways of behaving – our ways of life, everything we’ve known has been entirely interrupted.
For me, as a type 7 on the Enneagram, it’s all too easy to engage in the future, to think about the ‘what next?’, to avoid the pain of the here and now, by letting my imagination run wild of what the world might be like instead. But we cannot and must not miss the vital part of our current journey, which is to recognise, embrace and partake in the grieving process. Grief is not comfortable, it is not easy, it is not enjoyable – in fact it is both tumultuous and painful…..but it is good. Refusing to enter into it, or trying to suppress it, will only lead to a deepening of the trauma and a delay of this inevitable experience.
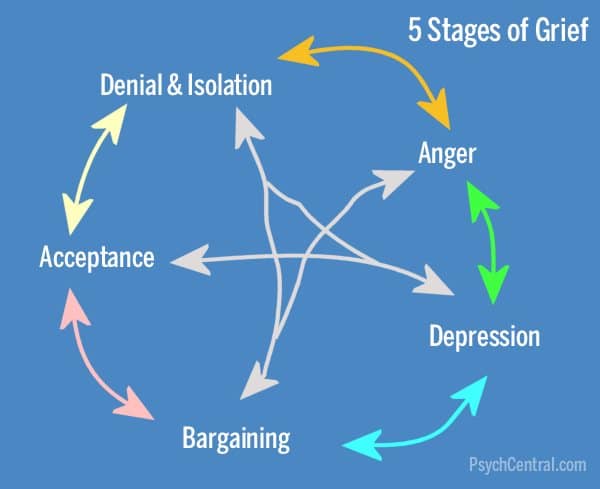
The thing about grief is that it is unpredictable and what makes it even more so in this current experience is that it is both personal and corporate. However, the cycle of grief is well known and although each of us will go through the cycle differently, it’s worth recognising where in the cycle we might be, both as individuals and as a wider community/society.
This is the classic ‘grief cycle’ (I’ve borrowed the graphic from psychcentral.com) and it demonstrates well how the experience of grief is neither straightforward nor easy. However, psychologists agree that each of us will pass through each of these phases, no matter how briefly – though we can remain stuck in some areas for quite some time.
The isolation of this time has been the starting place for most of us. For some that was coupled with an acceptance that we are where we are, but for others there was a denial that this could be real and a refusal to engage with the idea of social distancing (although with police enforcement, this quickly began to change!).
The anger phase is clearly present for many at the moment, and understandably so. Anger is not wrong, it’s how we respond to it that becomes the issue. Sadly, in many households we’re seeing a rise in Domestic Violence , particularly towards women and children and this is something we need to take really seriously. Learning to control our anger and find a positive outlet for it is absolutely key. There are all kinds of online resources to help with this, but the deep cuts to social services and policing over recent years have made it difficult to work with families in a more proactive way. The Violence Reduction Unit in Lancashire, led by Detective Chief Superintendent Sue Clarke, who is a brilliant leader, have done some incredible work in this area over the past couple of years, which is well worth learning from. The approach is much more productive than traditional methods of dealing with this issue and involves being with families more proactively to bring restoration and redemption into broken situations.
We’re also seeing the rise of a corporate anger. Tony Blair stated the other day that this is the most difficult time to contemplate being in government, and it’s true that we are in unprecedented times, but he feels our response nationally was slow. However, many feel that more serious questions, now being asked across the media spectrum, still need an answer:
- Were the government really prepared for this crisis? Why didn’t they take their practice run a few years ago more seriously?
- Why have we been so slow to roll out wider testing?
- Why is the death toll in the UK so much higher than a similar sized nation, like Germany?
- Why did our entire national response seem slow – what of the questions raised by the Sunday Times?
- What have the effects of 10 years of austerity been on the capability of public health teams, local government, social services and the NHS to respond to the situation we are now in?
- What did actually happen around the PPE debacle?
- Why is it that NHS and care workers are expected to put themselves at significant risk whilst caring for our those who are sick, without protective equipment?
- Why have a significant number of NHS workers died, particularly from BAME backgrounds?
- Why is it that more than 50% of all care workers in the UK are on less than minimum wage? Why don’t we value this work more highly?
- What is being done to protect the highly vulnerable children who are not attending school (only 5% of those classed as vulnerable have been attending)?
- Are the loans promised to businesses to help them survive coming about fast enough or getting to where they need to go?
- What about food poverty and the reality that many families can’t feed themselves?
These are all important questions that require an answer. Anger can be used to facilitate the right kind of conversations to bring challenge to the status quo and demand that it never leads us here again. The outcomes we are seeing were not inevitable – so what will we learn? What will be different? How will we change? If people in positions of power are willing to own up to mistakes, are we willing to forgive? I hope so…..how do we rebuild society otherwise? We must be able to learn and change our ways. It’s at the heart of what it means to love. But we must also recognise that some of this anger is simply part of the grief cycle and there may be no answers. We’re angry in part, because we are grieving. Sometimes our anger brings challenge and change, but sometimes we yell into the night and are met with silence.
Depression in grief can become clinical depression, but the word, in the context of grief, more describes a sense of deep sadness, loss, numbness, apathy and is often accompanied by tears. We must not try and keep a stiff upper lip, or push this away. Some of us will feel this more acutely than others, depending on our personality type, but this is a vitally important part of the process. This deep sadness can catch us unawares. It can come almost out of nowhere and we can find ourselves having a good cry in the bath or struggling to find the motivation to get out of bed of a morning. Talking about these feelings is absolutely vital, and it’s important that those of us who listen, ensure that the person experiencing these emotions feels heard. They don’t need fixing. They need validating. They need to know it’s OK to feel like this. We can’t just wish it away or get back on with things. There is a certain wallowing in this place that is extremely healthy and right. It’s true, we don’t want to get stuck here, and by putting some positive measures in place, like exercising, eating well, mindfulness and keeping a positive sense of routine, we can avoid becoming more mentally unwell. However, we must not try and rush through this phase or refuse to embrace the pain of it. But this can become a very dark experience and some people will wonder if life is even worth living. We can find ourselves asking searching questions: Can we really go on without our loved one? Will we ever get through the brokenness of this current situation, when we have lost so much? If this becomes overwhelming or there are serious thoughts of not wanting to carry on with life, this is where therapeutic interventions or medical treatment in the form of medication can be really important and literally life-saving.
At a corporate level, we share a sadness that 20000 people in the UK and 200000 people globally have lost their lives so far, due to COVID-19 – and that is just the recorded deaths. We will potentially feel lost that a whole way of being together is no longer possible, nor perhaps, desired. The artists will help us the most here. Songwriters, painters, choreographers and playwrights. Are we mature enough to embrace the songs and dances of lament? DO we know how to do this?
Bargaining is about us trying to begin to formulate some meaning or sense of what has happened/is happening. We might find that we want to talk about our experiences more, tell our stories, reach out to others and explore some of the ‘why’ questions we’re wrestling with. We might find we start ‘big conversations’ with God or ‘the universe’ – some thing like – ‘if you help me get my job back, then I’ll live a good life from now on’ or we might find we’re dealing with several regrets in our interactions or relationship with the person we have lost.
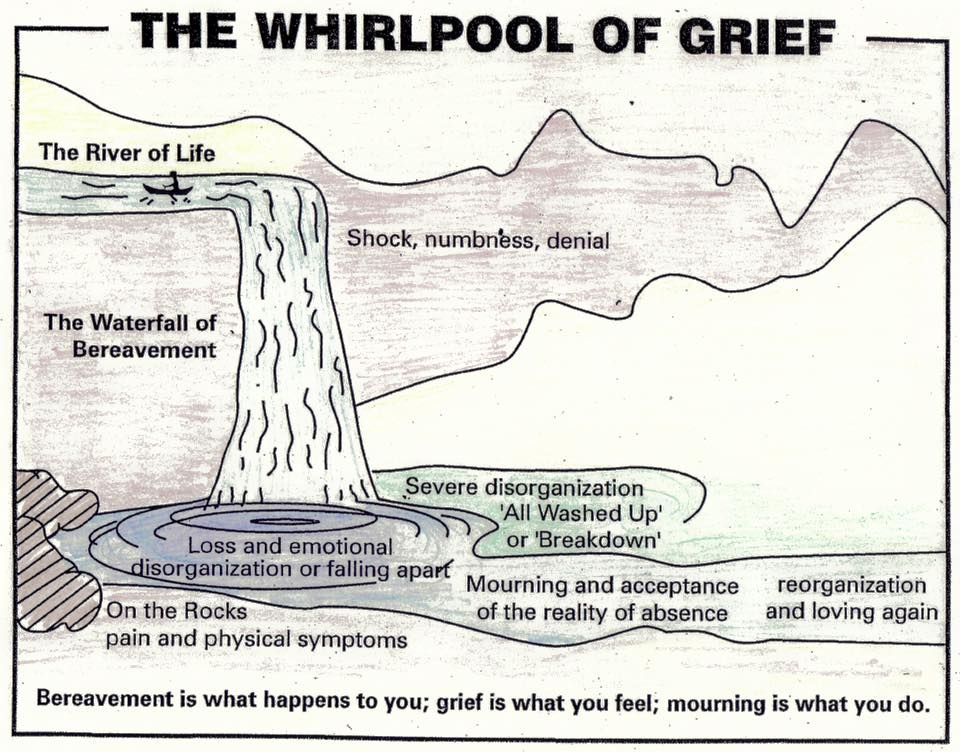 Acceptance is about realising that we are where we are and we cannot change a thing. It allows us to breathe deeply into the reality of the horrors we have walked through and begin to face into the future. Some people think of the grief cycle as more like a river with the grief cycle being a whirlpool that we get stuck in for a while. We go round and round, but eventually we come out the other side. On a personal level, perhaps, before we entered the whirlpool, we had a dearly loved one in our boat with us and we entered this whirlpool once that person became sick or was no longer in the boat with us, because they had died. The whirlpool can feel overwhelmingly difficult, with the stages above. We come out of the whirlpool with an acceptance that this dearly loved person is no longer in the boat with us….but there are other boats that we travel alongside, and perhaps there are others who still remain in our boat. We must now learn to live in this boat, without the person who was with us before but knowing we can face the future with our other companions. At a corporate level, this is about us sense making that the future cannot be like the past. Things have fundamentally changed. We cannot go back to how things were and so together we can build an altogether fairer and kinder future for our global population and the planet we inhabit together. This becomes what some refer to as the 6th stage of grief – ‘Meaning’. We begin to make sense of what we have journeyed through and use it to transform our experience of the world and how we want to live in it. My next blog will explore some of the meaning we may find the other side of COVID-19.
Acceptance is about realising that we are where we are and we cannot change a thing. It allows us to breathe deeply into the reality of the horrors we have walked through and begin to face into the future. Some people think of the grief cycle as more like a river with the grief cycle being a whirlpool that we get stuck in for a while. We go round and round, but eventually we come out the other side. On a personal level, perhaps, before we entered the whirlpool, we had a dearly loved one in our boat with us and we entered this whirlpool once that person became sick or was no longer in the boat with us, because they had died. The whirlpool can feel overwhelmingly difficult, with the stages above. We come out of the whirlpool with an acceptance that this dearly loved person is no longer in the boat with us….but there are other boats that we travel alongside, and perhaps there are others who still remain in our boat. We must now learn to live in this boat, without the person who was with us before but knowing we can face the future with our other companions. At a corporate level, this is about us sense making that the future cannot be like the past. Things have fundamentally changed. We cannot go back to how things were and so together we can build an altogether fairer and kinder future for our global population and the planet we inhabit together. This becomes what some refer to as the 6th stage of grief – ‘Meaning’. We begin to make sense of what we have journeyed through and use it to transform our experience of the world and how we want to live in it. My next blog will explore some of the meaning we may find the other side of COVID-19.
Whatever your experience of grief at this time, embrace it and talk about it, but don’t try and hurry it away. Good grief is a part of life and enables to process our loss, feel our pain, heal our wounds, accept our scars and find a new future. The ‘Good Grief’ movement is something I would really recommend exploring, especially if you are struggling to process your own grief. There is also lots of mental health support available through your local GP or online via nhs.uk. Grieving allows us not only to engage with the pain we are going through, but allows us to let go, so that we can reset and rediscover a way forward together. It’s impossible to walk through it alone, which is why as the city of Liverpool reminds us in the amazing song, sung at Anfield, friendship is everything.