 A Culture of Joy is the biggest determinant of safe and high quality healthcare! That is such a phenomenal statement that it is worth reading over and over again, making it into a poster, sticking it on your wall and meditating on it morning and night. It feels to be simultaneously absolutely true and somehow beyond belief. I’ve previously blogged here about the need for a culture of kindness in the NHS, and I hold to that – kindness certainly doesn’t exclude joy (!), but a Culture of Joy….. I don’t know, in a day in which 50% of our staff admit to feeling burnt out, can we honestly say we have developed this throughout our health system in the UK? So, what does it take to build this? How do we have a joyful workplace? If it is really the single largest factor affecting patient safety, which research from The Mayo Clinic, The IHI and The Quality Forum tell us it is, then we better sit up, pay attention and do something about it!
A Culture of Joy is the biggest determinant of safe and high quality healthcare! That is such a phenomenal statement that it is worth reading over and over again, making it into a poster, sticking it on your wall and meditating on it morning and night. It feels to be simultaneously absolutely true and somehow beyond belief. I’ve previously blogged here about the need for a culture of kindness in the NHS, and I hold to that – kindness certainly doesn’t exclude joy (!), but a Culture of Joy….. I don’t know, in a day in which 50% of our staff admit to feeling burnt out, can we honestly say we have developed this throughout our health system in the UK? So, what does it take to build this? How do we have a joyful workplace? If it is really the single largest factor affecting patient safety, which research from The Mayo Clinic, The IHI and The Quality Forum tell us it is, then we better sit up, pay attention and do something about it!
There are 3 key ingredients to creating a culture of Joy. The first (and this is in no sense a hierarchical order!) is leadership, the second is how 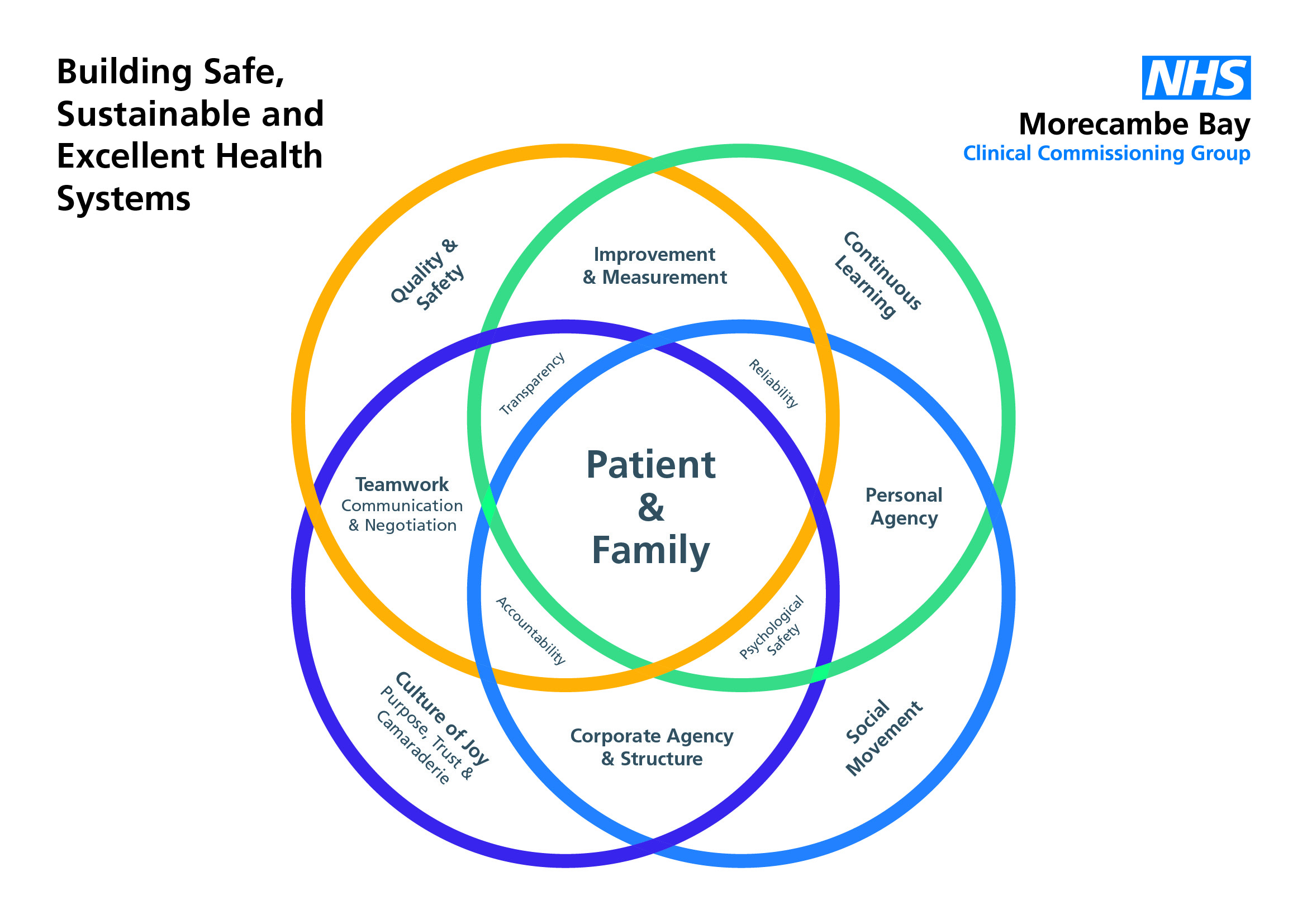
teams actually function together and the third is personal responsibility. You will see the words incorporated from the ‘culture circle’ in bold!
Good Leadership: Here’s a fascinating fact, I learnt from Stephen Swensen, of The Mayo Clinic – The bigger the signature of a CEO, the worse the outcomes for patients, staff and the finances of the organisation!! CEOs are responsible for setting the structures in place that allow healthy cultures to develop. Leaders create a culture of joy by having humility and developing 5 key behaviours:
- Appreciation – good leaders build joy in their teams by saying ‘Thank You’ – it is one of the things the team at my surgery consistently tells us, as partners. Of course we are grateful, but we don’t say it enough. Every member of a team knowing that they have value is so vital. I remember, as a house officer on a medical ward watching a lady called Jean, cleaning the ward and saying hello to all the patients. I went up to her and said, “Jean, I just want to thank you for everything you do on this ward, every day. The way you keep this place clean helps fight off infections and keeps people well; and the smile and kindness you bring is really comforting to people who are scared or hurting.” To my great surprise, she burst out crying. I asked her what was wrong and she told me that she had worked on this ward for 25 years and no-one had ever said ‘Thank You’ to her. My favourite hashtag on twitter is trybeinggrateful – it costs so little.
- Transparency – good leaders communicate openly with their teams. They don’t do ‘special huddles’ in which they invite a few ‘high level’ people to know their secrets. No. They communicate with honesty and openness and this builds trust. And with trust they are able to negotiate difficult situations and requests of their teams, because there is a belief that everyone is in it together.
- Ideas – They look to their teams for ideas. One of the things I loved learning about recently is that the CEO of Toyota in Derby, deliberately does not park his car in the special ‘CEO parking space’ right next to the building. Instead, he parks it at the far end of the factory, so that the walk to his office takes him through every department, (a good 30 minutes of his time), so he he can say “hi” to his staff, connect with them and ensure that he is hearing about their ideas for innovation and improvement. Toyota takes 2.5 million suggestions from its staff every year. This simply doesn’t happen enough in the NHS, and I wonder how many CEOs take time at the start of the day, to walk the corridors, listen to patient stories, understand the pressures in the ED, hear the heartbeat of the wards and get a sense of the ideas brewing in some of the most compassionate, caring and intelligent staff of any organisation in the UK. If we are to transform the NHS into a system that is truly safe, sustainable and excellent, we must listen more to the ideas of our teams and in doing so, we will cut waste, undo the reems of red tape and instead find we are working far more effectively and efficiently. To embed this into the culture, there must be psychological safety – that means that no question is too stupid, no idea is too dumb and it is safe to bring to attention concerns a person may have, without a fear of retribution. One great question for leaders to ask is, “what are the pebbles in your shoes?’ – in other words, what matters to you? Or what are the barriers for you here? What’s getting in the way? Great CEOs do not have great answers, they are willing to work with complexity and have great questions!
- Career Mentorship – every person needs to be able to keep learning and develop in their role. We all need mentors or coaches at different stages in our careers, and ensuring these structures are in place to support staff as the complexity and pressure we deal with increase, is vital in building joy. People who are developing in their role are naturally safer in their role.
- Inclusiveness – To a good leader, it doesn’t matter who you are, what you look like, what you believe, what your sexual orientation or
 status might be. You need to know that you are welcome and you are loved just as you are. Inclusive teams that do not scapegoat, do not sideline and do not bully are joyful teams. Joyful teams celebrate difference and thrive off it.
status might be. You need to know that you are welcome and you are loved just as you are. Inclusive teams that do not scapegoat, do not sideline and do not bully are joyful teams. Joyful teams celebrate difference and thrive off it.
Joyful Teams: It’s really important to understand that joy does not mean false happiness. It does not mean that we walk around with fake smiles on our faces all the time and pretend that everything is ok. Joy is much deeper than that. We deal with very sad and difficult things in our workplaces every single day. We break bad news, we hold people as they take their final breaths, we watch people make terrible life choices, we see and carry the hurt of those who suffer loss and each of us has our own burdens we carry from the lives we live outside of work. Joyful teams do not pretend like that stuff isn’t happening every day – quite the opposite. Joyful teams develop three key qualities:
- Camaraderie. The high school musical song – ‘We’re all in this together’ is a great theme tune for NHS teams. People need to know that they belong, that they are loved and that people care about them. On good days, we celebrate together, on bad days, we pull together. Joyful teams develop encouragement, support and kindness in how they treat each other.
- Purpose. Joyful teams have a real sense of shared vision and purpose. They know what they are there to do and each person knows that they are valued in that team. The posh term for this is a sense of corporate agency. This is our job to do, we are responsible for what happens here and we want to do our work with excellence.
- Trust. It is really important that individuals feel trusted to do their job without feeling like they are always being watched or criticised or that they have to give an account for every action. When people feel trusted, they actually work more effectively and produce better outcomes.
 Personal Responsibility: in order to create a culture of joy, it is not just the responsibility of the CEO or team leader, nor the atmosphere created by the team as a whole – we each have a responsibility to steward and hold to this culture. And that means taking care of our own needs. We need to be active, eat well, take notice, be mindful, sleep well, forgive those who hurt us and have good friendships. Making sure that we ‘host ourselves’ well, ensures that we play our part in building the culture of joy that is so vital to the providing care that is of the highest quality and safety. There is a personal accountability to ourselves and to those we work with to ensure this is so. There is also personal agency that rises to the challenge that each one of us can set a new trend and make a significant difference to the culture in which we work.
Personal Responsibility: in order to create a culture of joy, it is not just the responsibility of the CEO or team leader, nor the atmosphere created by the team as a whole – we each have a responsibility to steward and hold to this culture. And that means taking care of our own needs. We need to be active, eat well, take notice, be mindful, sleep well, forgive those who hurt us and have good friendships. Making sure that we ‘host ourselves’ well, ensures that we play our part in building the culture of joy that is so vital to the providing care that is of the highest quality and safety. There is a personal accountability to ourselves and to those we work with to ensure this is so. There is also personal agency that rises to the challenge that each one of us can set a new trend and make a significant difference to the culture in which we work.
In the midst of all we are currently facing in the NHS, for the sake of our patients and their families, it is vital that we build cultures of joy now and cultivate them for the future.








